Quality control of mRNA medications using LC-MS
A novel analytical platform based on isotope dilution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and automated software analysis has been developed by researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University (Japan) and RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) (Kyoto, Japan). The platform facilitates the quantitative characterization of long, modified mRNAs through comparison with a stable isotope-labelled reference.
mRNA- based medicines have been integral in treating various types of cancer and genetic diseases, but have become well-known globally due to their effectiveness as the primary component of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. In contrast to competing technologies, mRNA-based therapeutics are easy to scale up and manufacture and are considered to be low risk as they do not become integrated into the host cell’s genome.
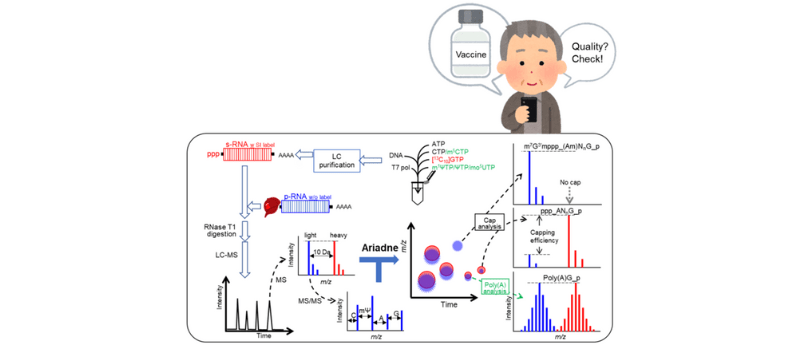
The recent demand for mRNA therapeutics globally has inspired much needed research into the development of effective quality control measures for these therapeutics. Lead by Dr Masato Taoka, Tokyo Metropolitan University and Hiroshi Nakayama, RIKEN CSRS, a research team has successfully developed an analytical platform that combines isotope dilution LC-MS and automated software analysis to quantitatively characterize long, modified RNAs. To achieve this, the modified RNAs are compared to a stable isotope-labelled reference with an identical base sequence.
You may also be interested in:
- mRNA COVID-19 vaccines linked to myocarditis in small subset of patients
- New software automates RNA analysis during research and development
- eBook: vaccine development in clinical trials
The team used the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine as the focus of their study. The mRNA strand used in these therapeutics have three common structural elements; a capping structure at the 5′ end, a specific base sequence and a polyadenylated (poly (A)) tail at the 3′ end. Although the platform, like others, can validate the modification of the specific sequence of the RNA reagent, the novelty of this platform is it’s ability analyze the capping structure and poly (A) tail.
The automated analysis uses Ariadne software and an mRNA sequence database. The platform performs database searching by utilizing the mass spectra as a query, allowing confirmation of the primary structures. Rapid identification of minute changes to the mRNA sequence can be achieved, whilst yielding quantitative information on the capping and poly (A) tail.
The platform can be used for a multitude of mRNA sequences of differing lengths and is a promising tool for quality control checking of mRNA vaccines and other medicines.






